![]()
![]()
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||
|
|
|
||||||||
|
|
Irrational number e |
|
|
|
Consider the binominal expansion of (1 +
When n tends to infinity,
The coefficient of the general term(the (r+1)th term) is :
We take When x = 1, we have or where
Discovery of Natural Logarithms 自然對數的發現 Consider a function If we change the base of the logarithm from a to e, we
have The logarithm with base e is called Natural Logarithm. Therefore, when Hence, or
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
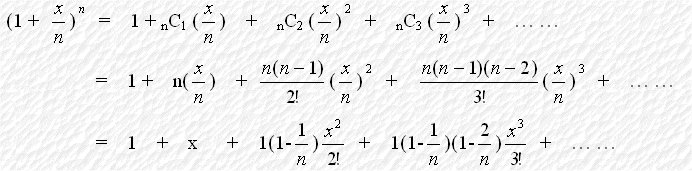
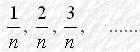 tend to zero. Also, n! =
tend to zero. Also, n! = 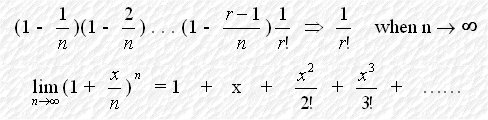
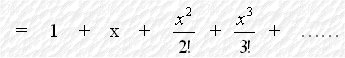
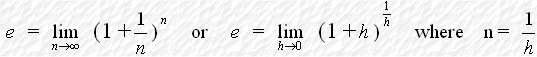
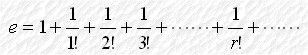
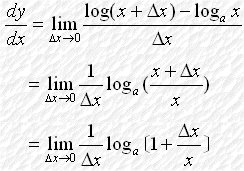
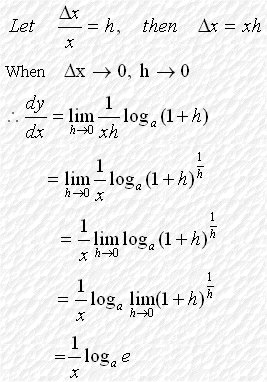
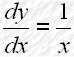
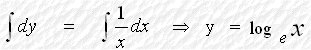 + C
+ C